Lecture 16
(Previous lecture) ... (Next lecture)
Fast Sequence Database Searches (BLAST)
...
Add:
- Summary points
- Exercises
- Further reading
Lecture Slides
Slide 001
Slide 002
Slide 003
Slide 004
Slide 005
Slide 006
Slide 007
Slide 008
Slide 009
Slide 010
Slide 011
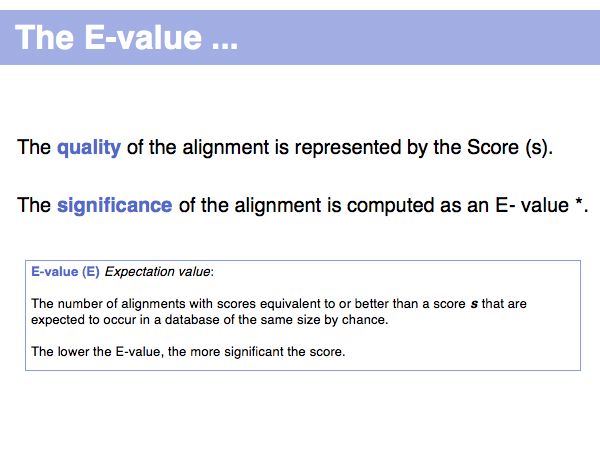
Lecture 16, Slide 011
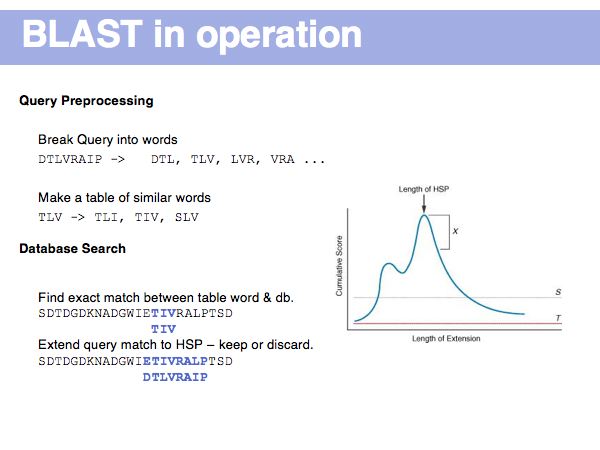
(*) Computing E-values is possible for HSPs since the statistcs of gap-less alignments are analytically tractable. Similar conclusions in general cannot be drawn from gapped alignments. Note the E-values are not a statement about the retrieved hit, but a statement about an expected distribution of scores. Or, to rephrase this, a poor e-value does not mean that your hit is not a homologue, but it means that at that score an irrelevant sequence has a a high chance of scoring well due to chance similarities.
(*) Computing E-values is possible for HSPs since the statistcs of gap-less alignments are analytically tractable. Similar conclusions in general cannot be drawn from gapped alignments. Note the E-values are not a statement about the retrieved hit, but a statement about an expected distribution of scores. Or, to rephrase this, a poor e-value does not mean that your hit is not a homologue, but it means that at that score an irrelevant sequence has a a high chance of scoring well due to chance similarities.
Slide 012

Lecture 16, Slide 012
(*) Note that restricting by organism is not a restriction on the search, but a restriction on the list of results that are being reported. The search takes just as long. Many databases of model-organism genome projects offer BLAST searches on their specific data. These may be faster.
(*) Note that restricting by organism is not a restriction on the search, but a restriction on the list of results that are being reported. The search takes just as long. Many databases of model-organism genome projects offer BLAST searches on their specific data. These may be faster.
Slide 013
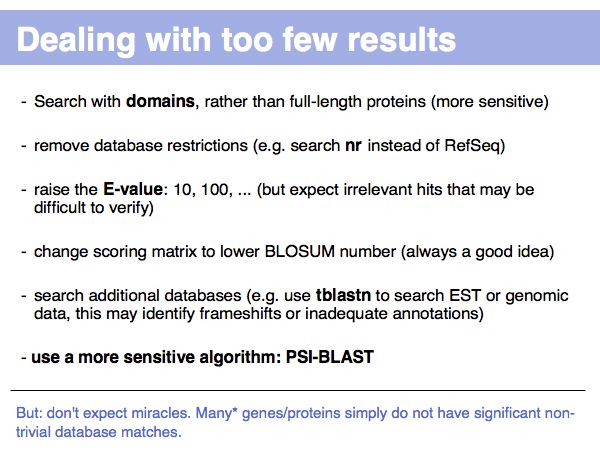
Lecture 16, Slide 013
(*) How many? That depends. Unknown genes (or "ORFans") may comprise a significant (albeit diminishing) fraction of genomes. See Siew&Fischer(2003) and the ORFan database
(*) How many? That depends. Unknown genes (or "ORFans") may comprise a significant (albeit diminishing) fraction of genomes. See Siew&Fischer(2003) and the ORFan database