BioCyc
BioCyc
BioCyc is a collection of metabolic pathways databases, derived from computational annotation (and manual curation) of whole-genome sequence data. The database range from highly curated (such as EcoCyc, and HumanCyc, and the comparative, multiorganism MetaCyc resource) to purely computationally derived.
Introductory reading
| Caspi et al. (2012) The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes and the BioCyc collection of pathway/genome databases. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D742-53. (pmid: 22102576) |
|
[ PubMed ] [ DOI ] The MetaCyc database (http://metacyc.org/) provides a comprehensive and freely accessible resource for metabolic pathways and enzymes from all domains of life. The pathways in MetaCyc are experimentally determined, small-molecule metabolic pathways and are curated from the primary scientific literature. MetaCyc contains more than 1800 pathways derived from more than 30,000 publications, and is the largest curated collection of metabolic pathways currently available. Most reactions in MetaCyc pathways are linked to one or more well-characterized enzymes, and both pathways and enzymes are annotated with reviews, evidence codes and literature citations. BioCyc (http://biocyc.org/) is a collection of more than 1700 organism-specific Pathway/Genome Databases (PGDBs). Each BioCyc PGDB contains the full genome and predicted metabolic network of one organism. The network, which is predicted by the Pathway Tools software using MetaCyc as a reference database, consists of metabolites, enzymes, reactions and metabolic pathways. BioCyc PGDBs contain additional features, including predicted operons, transport systems and pathway-hole fillers. The BioCyc website and Pathway Tools software offer many tools for querying and analysis of PGDBs, including Omics Viewers and comparative analysis. New developments include a zoomable web interface for diagrams; flux-balance analysis model generation from PGDBs; web services; and a new tool called Web Groups. |
Contents
...
Exercises
| Latendresse et al. (2012) Browsing metabolic and regulatory networks with BioCyc. Methods Mol Biol 804:197-216. (pmid: 22144155) |
|
[ PubMed ] [ DOI ] The BioCyc database collection at BioCyc.org integrates genome and cellular network information for more than 1,100 organisms. This method chapter describes Web-based tools for browsing metabolic and regulatory networks within BioCyc. These tools allow visualization of complete metabolic and regulatory networks, and allow the user to zoom-in on regions of the network of interest. The user can find objects of interest such as genes and metabolites within the networks, and can selectively examine the connectivity of the network. The EcoCyc database within the BioCyc collection has been extensively curated. The descriptions within EcoCyc of the Escherichia coli metabolic network and regulatory network were derived from thousands of publications. Other BioCyc databases received moderate levels of curation, or no curation at all. Those databases receiving no curation contain metabolic networks that were computationally inferred from the annotated genome sequences of each organism. |
Further reading and resources
| BioCyc [ link ] [ page ] BioCyc is a collection of metabolic pathways databases, derived from computational annotation (and manual curation) of whole-genome sequence data. The database range from highly curated (such as EcoCyc, and HumanCyc, and the comparative, multiorganism MetaCyc resource) to purely computationally derived. Searches can be performed by component, reaction or pathway, and by ontology. The example URL leads to the cellulosome cellulose degradation pathway in MetaCyc. | 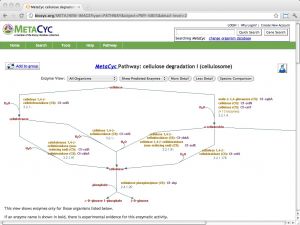 |