Difference between revisions of "Tools Exam Questions"
(→2002) |
|||
| Line 129: | Line 129: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| + | <!-- | ||
==2002== | ==2002== | ||
[[Image:Stereo_000000.jpg|frame|none|Caption. ]] | [[Image:Stereo_000000.jpg|frame|none|Caption. ]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Explanation ... | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
<div style="padding: 5px; background: #DDDDDD; border:solid 1px #000000;"> | <div style="padding: 5px; background: #DDDDDD; border:solid 1px #000000;"> | ||
| Line 140: | Line 146: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | --> | ||
Revision as of 15:32, 11 December 2006
One aspect of bioinformatics concerns algorithms: computational tools that allow us to analyse the data and support our inferences.
2003
WWW servers for the multiple alignment program T-Coffee require only a set of sequences as input for their task. Obviously, the important parameters the program uses are hidden - they have been set to a reasonable default.
- Briefly discuss the key parameters that such a program needs and how they influence the result.
2003
- " Magnaporthe grisea, the causal agent of rice blast disease, is one of the most devastating threats to food security worldwide. Conservatively, each year enough rice is destroyed by rice blast disease to feed 60 million people [...]. Indeed, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has recently recognized and listed rice blast as a significant biological weapon. No part of the world is now safe from this disease. It was long thought of as being confined to developing nations, but over the past decade it has emerged as a serious problem in the United States. [...] Widespread devastation of golf courses, particularly in the Midwest, where it has been attacking cool season grasses, is of particular concern. "
[... excerpt from the Web pages of the US Magnaporthe grisea genome project of the Center for Genome Research]
In an effort to annotate the M. grisea genome, you have done a BLAST search of the E. coli Glutaminyl tRNA synthetase gene against the predicted M. grisea open reading frames: your goal is to find the orthologue of this gene. You have chosen the "nr" database and have limited the search output to magnaporthe grisea"[organism] in the appropriate advanced-options field of the Web form. Here are excerpts from the output you receive:
Sequences producing significant alignments: (bits) Value gi|38104873|gb|EAA51376.1| hypothetical protein MG09393.4 [... 391 e-109 gi|38106536|gb|EAA52828.1| hypothetical protein MG05956.4 [... 268 3e-72 gi|38106250|gb|EAA52583.1| hypothetical protein MG05275.4 [... 59 2e-09 gi|38101579|gb|EAA48524.1| hypothetical protein MG00182.4 [... 30 1.7
- Comment briefly on each of the portions of the above excerpt from the BLAST output, that is formatted in bold and red.
>gi|38106250|gb|EAA52583.1| hypothetical protein MG05275.4 [Magnaporthe grisea ]
Length = 594
Score = 59.3 bits (142), Expect = 2e-09
Identities = 61/243 (25%), Positives = 102/243 (41%), Gaps = 34/243 (13%)
Query: 30 TRFPPEPNGYLHIGHAKSICLNFGIAQDYKGQCNLRFDDTNPVKEDIEYVESIKNDVEWL 89
TRF P P G+LH+G ++ N+ +A+ GQ LR +DT+ + + + D+ W
Sbjct: 61 TRFAPSPTGFLHLGSLRTALFNYLLAKATGGQFLLRLEDTDRTRIVPDAEARLYQDLRWA 120
Query: 90 GFHW---------SGNVRYSSDYFDQLHAYAIELINKGLAYVDELTPEQIREYR-GTLTQ 139
G W SG R S+ YA +L++ G AY T E++ + G+
Sbjct: 121 GLVWDEGPDVGGPSGPYR-QSERLGHYSKYAQQLLDSGRAYRCFCTREELAASQLGSQAD 179
Query: 140 PGKNSPYRDRSVEENLALFEKMRAGGFEEGKACLRAKIDMASPFIVMRDPVLYRIKFAEH 199
G Y + + E+ A G +R + + +PF V P L +F +
Sbjct: 180 SGAGGRYPGTCLAVSADESEERAARG---DAHVIRFRSN-TTPFTV---PDLVYRRFRKK 232
Query: 200 HQTGN----KWCIYPMYDFTHCISDALEGITHSLCTLEFQDNRRLYDWVLDNITIPVHPR 255
H + K +P Y F + + D L +TH + R +W+ I+ P+H
Sbjct: 233 HMEDDFIIMKSDGFPTYHFANVVDDHLMDVTHVI---------RGAEWL---ISTPMHCD 280
Query: 256 QYE 258
Y+
Sbjct: 281 LYD 283
- Briefly discuss what you can conclude about MG05275.4 from the above excerpt of the BLAST report.
- Describe at least two approaches for functional annotation that are not based on homology that you can use to annotate MG05275.4 ?
- Would the same search using PSI-BLAST rather than BLAST have helped for your task?
2003 - Clustal W
In order to run a multiple alignment from a Web interface to the ClustalW program, you are requested to specify a number of parameters.
- Briefly discuss gap and weight-matrix parameters, their relationship and sensible choices.
- Briefly list the key steps of the ClustalW algorithm.
2003 - PSI-Blast
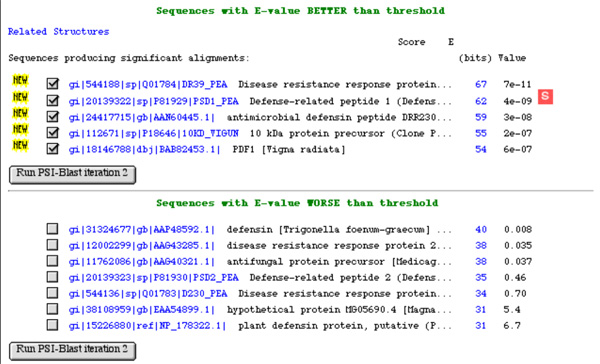
Defensins are small proteins of about 50 amino acids with a characteristic fold and disulfide bonding pattern. Plants have large families of defensins in their genome conferring resistance against fungal and bacterial pathogens. While resistance against fungi appears to involve specific binding to membrane targets, antibacterial effects seem to involve non-specific membrane permeabilization. In order to establish the relative importance of specific binding to target proteins and non-specific, physicochemical mode of action, you reason that specific binding should be compromised when you change defensin sequences towards the consensus sequence, while the non-specific effects should be enhanced. You thus decide to perform a sensitive PSI-BLAST search with the sequence of pea defensin I, as a basis for the multiple alignment of defensin sequences, in order to obtain a consensus sequence of defensin orthologs.
As you know, PSI-BLAST (Position Specific Iterated ...) scans a sequence database with a BLAST search, then builds a profile from the similar sequences it retrieves and repeats the search, then repeats this procedure, refinining the profile at every step, until no more sequences can be added.
- What key steps has the program gone through at this stage ?
- What is the "E-value" that is referred to here ?
- What will the program do in iteration 2 ?
- What input can you give the program before running iteration 2 and why is it necessary to manually adjust the input (i.e. what happens if a false positive is selected )?
- Which of these sequences are probably homologs to your query ? Explain.
Here is an excerpt from the alignments this PSI-BLAST search has produced in its first round:
gi|15226880|ref|NP_178322.1| plant defensin protein, putative (PDF2.6)
gi|11387216|sp|Q9ZUL8|THG4_ARATH Gamma-thionin homolog At2g02140 precursor
gi|25330850|pir||D84433 proteinase inhibitor II [imported] - Arabidopsis thaliana
gi|4038038|gb|AAC97220.1| protease inhibitor II [Arabidopsis thaliana]
gi|21592674|gb|AAM64623.1| protease inhibitor II [Arabidopsis thaliana]
Length = 73
Score = 30.8 bits (68), Expect = 6.7
Identities = 14/46 (30%), Positives = 27/46 (58%), Gaps = 1/46 (2%)
Query: 1 KTCEHLADTYRGVCFTNASCDDHCKNKAHLISGTCHNWKCFCTQNC 46
+TCE ++ ++GVC + SC C ++ G C + +C+C++ C
Sbjct: 29 RTCESPSNKFQGVCLNSQSCAKACPSEG-FSGGRCSSLRCYCSKAC 73
gi|15226880|ref|NP_178322.1|is a piece of hypertext with a link. What does the link lead to?- What is a "gi" and what is a "ref" ?
- Why are there five records in front of one alignement here that begin with "gi|..." ?
- What does "Expect = 6.7" mean ?
- Are the two genes that "Query" and "Sbjct" refer to homologous ? Explain.
- Should you include this protease inhibitor in your next iteration of PSI-BLAST ? Why or why not?