Difference between revisions of "User:Boris/BCB hackathon 2018"
m |
m (→Background) |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
<table style="Cellpadding:10px;"> | <table style="Cellpadding:10px;"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td style="padding-right:10px" width="50%"> |
The first two draft sequences of the human genome were published in February of 2001<ref>{{#pmid: 11237011}}</ref><ref>{{#pmid: 11181995}}</ref>. Three years from now will mark the twentieth anniversary of this accomplishment that like now other has shaped the landscape of bioinformatics, computational biology and molecular medicine. In 2001, {{WP|Celera}} - a private company founded three years earlier to commercialize genome information - published an iconic poster summarizing their version of the genome. | The first two draft sequences of the human genome were published in February of 2001<ref>{{#pmid: 11237011}}</ref><ref>{{#pmid: 11181995}}</ref>. Three years from now will mark the twentieth anniversary of this accomplishment that like now other has shaped the landscape of bioinformatics, computational biology and molecular medicine. In 2001, {{WP|Celera}} - a private company founded three years earlier to commercialize genome information - published an iconic poster summarizing their version of the genome. | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td style="padding-right:10px"> |
This poster is significant, not so much for its interpretable content, but for the unique perspective it gives us on the entirety of information that constitutes our molecular identity. | This poster is significant, not so much for its interpretable content, but for the unique perspective it gives us on the entirety of information that constitutes our molecular identity. | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td style="padding-right:10px"> |
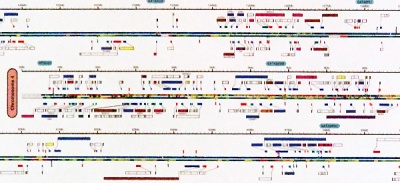
The details are rich, in fact, surprisingly "modern", presenting features like CpG islands and SNP density, and exon transcripts with Gene Ontology functional categories colour coded, for forward and reverse strand, accurately plotted on the nucleotide backbone at about 500 kB per centimetre. This was computed from gff records with Josep Abril's <code>gff2ps</code> software<ref>{{#pmid: 11099262 }}</ref>. | The details are rich, in fact, surprisingly "modern", presenting features like CpG islands and SNP density, and exon transcripts with Gene Ontology functional categories colour coded, for forward and reverse strand, accurately plotted on the nucleotide backbone at about 500 kB per centimetre. This was computed from gff records with Josep Abril's <code>gff2ps</code> software<ref>{{#pmid: 11099262 }}</ref>. | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
Revision as of 01:48, 7 February 2018
BCB Hackathon 2018
(Topic Proposal: The Human Genome - 20 years later)
Abstract:
This topic proposal for the 2018 BCB hackathon is to explore new ways to provide a holistic overview of the contents of the human genome, for the occasion of the 20th anniversary of its sequence.
Contents
Background
|
The first two draft sequences of the human genome were published in February of 2001[1][2]. Three years from now will mark the twentieth anniversary of this accomplishment that like now other has shaped the landscape of bioinformatics, computational biology and molecular medicine. In 2001, Celera - a private company founded three years earlier to commercialize genome information - published an iconic poster summarizing their version of the genome. |
|
|
This poster is significant, not so much for its interpretable content, but for the unique perspective it gives us on the entirety of information that constitutes our molecular identity. |
|
|
The details are rich, in fact, surprisingly "modern", presenting features like CpG islands and SNP density, and exon transcripts with Gene Ontology functional categories colour coded, for forward and reverse strand, accurately plotted on the nucleotide backbone at about 500 kB per centimetre. This was computed from gff records with Josep Abril's |
But we know so much more today. The number of sequenced genomes has exploded - selected individuals at first, then we envisioned the 1,000 genomes project (2008, completed 2012); quickly set our sights on 100,000 genomes (2012, almost completed), and as of today more than 500,000 human genomes have been sequenced overall. We have sequenced cancers, and genetic diseases. We have sequenced representatives of virtually all ethnicities on the planet. We have even sequenced Neanderthals and Denisovians, and we have sequenced other species far and wide to acquire a sense of where we fit into the landscape of evolution. We have annotated the contents of the genome in the ENCODE project. We have built databases that carefully dissect all proteins into their domains, such as InterPro. We have started to outline how things work together in functional networks such as the STRING data, or in modules as published by KEGG, and we are beginning to translate our insights into actionable information for medicine, at the OICR, at Sick Kids' TCAG.
Our imagination of the genome has matured tremendously. What is the image we will find for it?
Goals
Process
Perspectives
Notes
- ↑
Lander et al. (2001) Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409:860-921. (pmid: 11237011) [ PubMed ] [ DOI ] The human genome holds an extraordinary trove of information about human development, physiology, medicine and evolution. Here we report the results of an international collaboration to produce and make freely available a draft sequence of the human genome. We also present an initial analysis of the data, describing some of the insights that can be gleaned from the sequence.
- ↑
Venter et al. (2001) The sequence of the human genome. Science 291:1304-51. (pmid: 11181995) [ PubMed ] [ DOI ] A 2.91-billion base pair (bp) consensus sequence of the euchromatic portion of the human genome was generated by the whole-genome shotgun sequencing method. The 14.8-billion bp DNA sequence was generated over 9 months from 27,271,853 high-quality sequence reads (5.11-fold coverage of the genome) from both ends of plasmid clones made from the DNA of five individuals. Two assembly strategies-a whole-genome assembly and a regional chromosome assembly-were used, each combining sequence data from Celera and the publicly funded genome effort. The public data were shredded into 550-bp segments to create a 2.9-fold coverage of those genome regions that had been sequenced, without including biases inherent in the cloning and assembly procedure used by the publicly funded group. This brought the effective coverage in the assemblies to eightfold, reducing the number and size of gaps in the final assembly over what would be obtained with 5.11-fold coverage. The two assembly strategies yielded very similar results that largely agree with independent mapping data. The assemblies effectively cover the euchromatic regions of the human chromosomes. More than 90% of the genome is in scaffold assemblies of 100,000 bp or more, and 25% of the genome is in scaffolds of 10 million bp or larger. Analysis of the genome sequence revealed 26,588 protein-encoding transcripts for which there was strong corroborating evidence and an additional approximately 12,000 computationally derived genes with mouse matches or other weak supporting evidence. Although gene-dense clusters are obvious, almost half the genes are dispersed in low G+C sequence separated by large tracts of apparently noncoding sequence. Only 1.1% of the genome is spanned by exons, whereas 24% is in introns, with 75% of the genome being intergenic DNA. Duplications of segmental blocks, ranging in size up to chromosomal lengths, are abundant throughout the genome and reveal a complex evolutionary history. Comparative genomic analysis indicates vertebrate expansions of genes associated with neuronal function, with tissue-specific developmental regulation, and with the hemostasis and immune systems. DNA sequence comparisons between the consensus sequence and publicly funded genome data provided locations of 2.1 million single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). A random pair of human haploid genomes differed at a rate of 1 bp per 1250 on average, but there was marked heterogeneity in the level of polymorphism across the genome. Less than 1% of all SNPs resulted in variation in proteins, but the task of determining which SNPs have functional consequences remains an open challenge.
- ↑
Abril & Guigó (2000) gff2ps: visualizing genomic annotations. Bioinformatics 16:743-4. (pmid: 11099262) [ PubMed ] [ DOI ] gff2psis a program for visualizing annotations of genomic sequences. The program takes the annotated features on a genomic sequence in GFF format as input, and produces a visual output in PostScript. While it can be used in a very simple way, it also allows for a great degree of customization through a number of options and/or customization files.
About ...
Last update:
- 2017-02-06
Version:
- 1.0
Version history:
- 1.0 First proposal
![]() This copyrighted material is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Follow the link to learn more.
This copyrighted material is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Follow the link to learn more.