Difference between revisions of "Stereo Vision Exam Questions"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

(→2004) |
(→2004) |
||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==2004== | ||
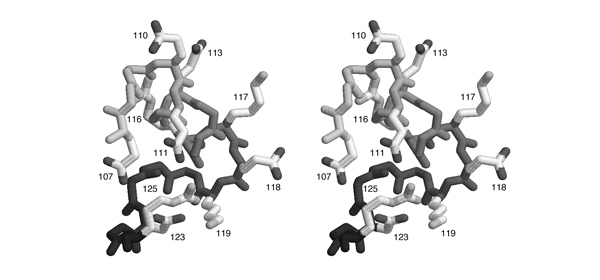
| + | [[Image:Stereo_GlnRS-SaltBridges.jpg|frame|none|This divergent stereo-view shows a subdomain of GluRS from ''Thermus thermophilus'' (1N78.PDB) that is rich in charged amino acids. Sidechains are shown for aspartate, glutamate, lysine and arginine residues. The backbone is shaded in grey from light (N-terminus) to dark (C-terminus). Sequence numbers are given next to the sidechains.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="padding: 5px; background: #DDDDDD; border:solid 1px #000000;"> | ||
| + | *'''List all pairs of residues that form salt-bridges according to this figure. Write the one-letter code for the negatively charged amino acid and its sequence number, then the same for the positively charged amino acid.''' | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <small>Comment</small> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==2004== | ||
| + | [[Image:Stereo-Gln-RS_BindingSite.jpg|frame|none|This divergent stereo-view shows part of the substrate binding site of a subdomain of GluRS from ''Thermus thermophilus'' (1N78.PDB), including the substrate analogon <u>glutamol-AMP</u>. The "<code>HIGH</code>" region is included here, its sequence is <code>HVGT</code> in this case. Carbons are shown in light grey, nitrogen atoms are darker, oxygen atoms are darkest grey and sulphur and phosphorous are black.]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="padding: 5px; background: #DDDDDD; border:solid 1px #000000;"> | ||
| + | *'''Based on this figure, argue briefly why "G" is a conserved residue in the "<code>HIGH</code>" motif. ''' | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
Revision as of 23:21, 11 December 2006
- Molecules are three-dimensional entities and stereo-vision of images on paper and on the screen is one of the most powerful, intuitive ways to appreciate that. We have practiced stero-vision in this course; here are a number of situations that require spatial awareness.
2002
- Write down the label of the tryptophan that is a conserved element of the hydrophobic core of this domain.
2002
- Trace the backbone from the N-terminus to amino acid 52 with pencil or pen in one of the images.
I wouldn't ask this type of question any longer - the drawing task seems a bit convoluted for the actual skill it is supposed to test.
2003
As you know, a strong dipole moment is generated from the synergistic interactions of carbonyl groups in alpha helices. The carbonyls point towards the negative potential.
- Which three alpha helices are oriented best, so that their helix-dipole moment is aligned for favourable interactions with the ATP phosphate groups?
2003
The figure was generated with the following RasMol commands:
set background white set stereo -5 select all color white restrict helix and backbone wireframe 90 select glu,asp color [80,80,80]
- Mark on this sheet the position of those Asp or Glu residues that are positioned to interact favourably with the helix dipole. If there are several plausible residues in a helix, mark the one closest to the correct terminus.
2003
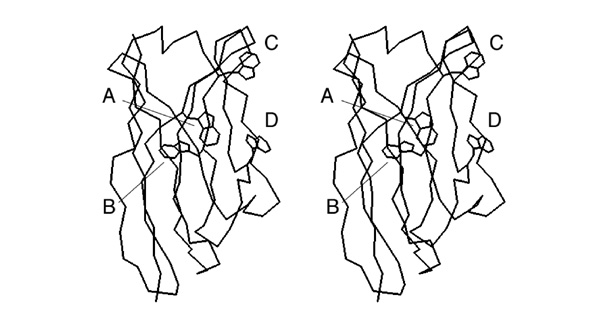
- Trace the disulfide bonded cysteine sidechains in one of the stereoviews of this picture.
2004
- Number the cysteines from 1 to 8, from N- to C- terminus and determine the disulfide bonding topology of this protein. Write the disulfide bonded residue pairs into your exam booklet.
2004

This divergent stereo-view shows a subdomain of GluRS from Thermus thermophilus (1N78.PDB) that is rich in charged amino acids. Sidechains are shown for aspartate, glutamate, lysine and arginine residues. The backbone is shaded in grey from light (N-terminus) to dark (C-terminus). Sequence numbers are given next to the sidechains.
- List all pairs of residues that form salt-bridges according to this figure. Write the one-letter code for the negatively charged amino acid and its sequence number, then the same for the positively charged amino acid.
Comment
2004

This divergent stereo-view shows part of the substrate binding site of a subdomain of GluRS from Thermus thermophilus (1N78.PDB), including the substrate analogon glutamol-AMP. The "
HIGH" region is included here, its sequence is HVGT in this case. Carbons are shown in light grey, nitrogen atoms are darker, oxygen atoms are darkest grey and sulphur and phosphorous are black.
- Based on this figure, argue briefly why "G" is a conserved residue in the "
HIGH" motif.